Introduction
In today’s fast-paced software development cycle, automation is not just a nice-to-have — it’s a critical enabler of speed, quality, and customer trust. Yet one of the most common challenges QA teams face is flaky tests. A small CSS change or UI tweak can break dozens of scripts, resulting in hours of rework and slowing down the release process.
At QualiTlabs, we’ve seen this problem across industries — from SaaS startups to global enterprises. Our solution? Custom test attributes: a simple yet powerful practice that makes your automation stable, scalable, and business-friendly.
Why Not Use IDs or Classes?
Without custom attributes, test scripts often rely on:
- CSS classes
- IDs generated by frameworks
- Nested XPaths
These are fragile. The result? Every UI change increases maintenance overhead, slows QA cycles, and delays releases.
Why use Custom test attributes
By adopting custom test attributes (data-test, data-qa, etc.), you gain:
- Stability – Tests no longer break when styling or layout changes occur, as they are created solely for testing purposes.
- Clarity – Attributes clearly document test intent for future engineers.
- Speed – Reduced maintenance = faster regression runs and quicker releases.
- Business impact – Less QA overhead and higher developer confidence.
Which Attribute Should You Use?
There’s flexibility depending on your project setup:
- data-test → Common and simple.
- data-testid → Popular in React Testing Library and Jest.
- Custom ones (e.g., data-qa, data-pw) → Supported in tools like Playwright.
👉 Tip: The exact name doesn’t matter as long as your team follows one consistent convention.
How to Name Test Attributes
Good naming makes your tests clear and future-proof. Follow these rules:
- Be descriptive → data-test=”login-button” instead of button1.
- Add context → data-test=”homepage-login-button”.
- Ensure uniqueness → Each element should have a unique value.
- Use a pattern → <page>-<element>-<purpose>.
Best Practices for Adding Attributes
- Don’t use them for styling → Keep them test-only.
- Automate attribute injection → In React or Angular, wrap components to auto-generate test IDs.
- Use consistent naming conventions
Example: data-test=”login-button”, data-test=”signup-email-input”. - Keep attributes human-readable
Descriptive names improve test readability and debugging. - Create selector helpers
Centralize selector logic in utilities for maintainability.
- Educate developers early
Involve dev teams so attributes are added as part of the coding standard. - Integrate across frameworks
Works seamlessly with Cypress, Playwright, and Selenium.
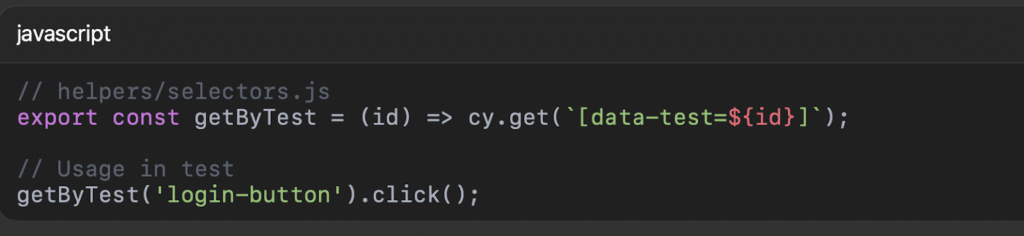
Example: Cypress Selector Helper
// helpers/selectors.js
export const getByTest = (id) => cy.get(`[data-test=${id}]`);
// Usage in test
getByTest(‘login-button’).click();
The above code should be formatted as follows.
💡 Real-World Example
HTML
<button data-test=”submit-button”>Submit</button>
Cypress
cy.get(‘[data-test=”submit-button”]’).click();
Playwright
await page.getByTestId(‘submit-button’).click();
Business Impact That Matters
- For QA Managers: Reduce test suite maintenance by up to 40%.
- For CTOs / Product Heads: Accelerate time-to-market without sacrificing quality.
- For Developers: Minimise QA bottlenecks and focus on innovation.
Custom test attributes are more than a technical trick — they’re a business enabler.
Try It Yourself — With QualiTlabs
Ready to make your automation resilient, AI-driven, and future-proof?
QualiTlabs offers a no-cost, 2-week AI QA pilot where you can experience:
- Our expert QA engineers
- The power of QBot™ – Your Manual Test Cases, Now AI-Executed Autonomously in hours.
- Your first 30 test scripts are automated at no cost
👉 Reach out at sales@qualitlabs.com and see how we can help your team deliver quality at the speed of modern AI-driven development.
Final Thought
Custom test attributes are the foundation of robust automation frameworks. Combined with QualiTlabs’ expertise and QBot™ innovation, they ensure your QA doesn’t just keep up — it drives business speed and reliability.

